Head and Neck
Salivary Gland Disorders
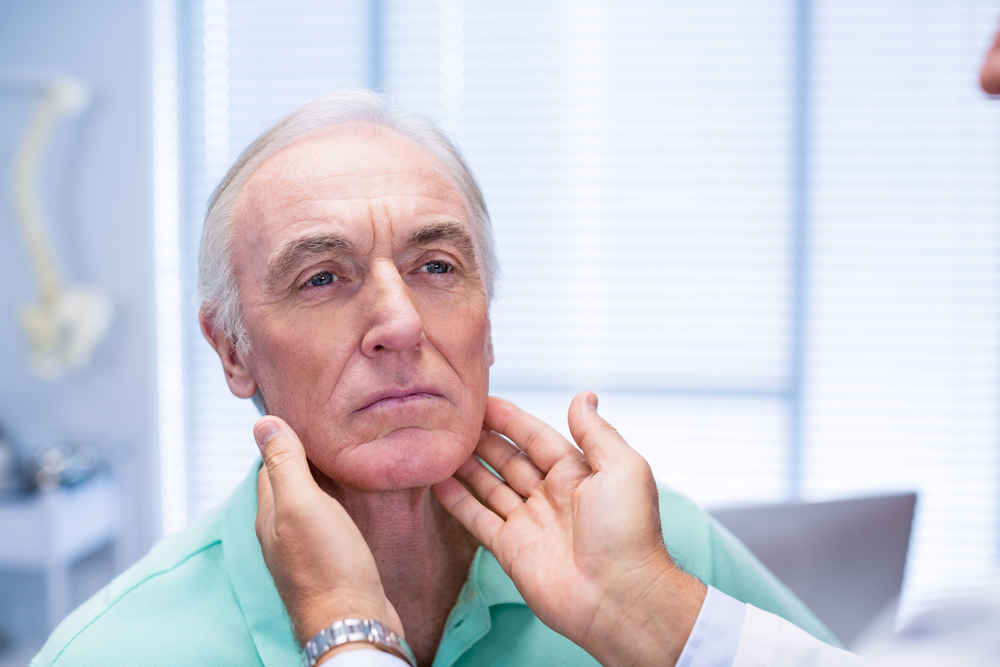
What are salivary gland disorders?
There are 2 main paired salivary glands within the human body – the parotid gland and the submandibular gland. Salivary gland disorders can range from inflammatory conditions to tumors. Symptoms may include: enlargement or discomfort within the associated salivary gland, dry mouth, bad breath or a foul taste in the mouth. Inflammatory conditions are typically secondary to blockages within the salivary gland itself, leading to decreased salivary flow and swelling of the gland and potential bacterial infections. A common cause of obstruction is salivary stones. Furthermore, salivary masses/tumors can also grow within the glands, with the majority being benign conditions but it is important to seek evaluation, as not all masses are benign.
How are salivary gland disorders treated?
Diagnosis begins with an office visit for a history and physical exam to determine the most likely source of symptoms. Further work-up may include radiographic imaging and needle biopsy. Treatment depends on the underlying cause with conservative managements including use of warm compresses, massages of the affected gland and sialagogues (i.e. chewing gum, sour items, etc.). If infected, oral antibiotics and corticosteroids may sometimes be necessary. More severe cases or tumors/masses may involve surgical management of the obstruction or removal of the mass/gland.
Thyroid Nodules
What are thyroid nodules?
Thyroid nodules are discrete growths within the thyroid gland that are common findings in adults, particularly in women and older individuals. The vast majority of nodules are benign, but a small percentage may represent thyroid cancer, making proper evaluation essential. Thyroid nodules typically present without symptoms, that may be incidentally noted routine physical exam and imaging. Rarely nodules result in overproduction of thyroid hormone that may lead to symptoms of hyperthyroidism. While symptoms are uncommon, they may include: neck fullness, difficulty swallowing, discomfort/pain, lymph node swelling and potentially voice changes/hoarseness.
How are thyroid nodules treated?
Proper evaluation of the thyroid nodules begins with the clinical history and then likely involves an ultrasound evaluation. If there is concern, a needle biopsy is performed. Otherwise, recommendation may be to monitor with repeat ultrasounds to ensure no change. Sometimes, surgical management with removal of portions of the thyroid or the gland in its entirety may be warranted.
Neck Masses
What are neck masses?
Neck masses can occur in both adults and pediatric patients. The majority of neck masses tend to be benign and can be the result of a variety of conditions including congenital (since birth), inflammatory, infectious and neoplastic (both benign and malignant tumors). Clinical history and evaluation is the first step, potentially followed by lab work or imaging studies.
How are neck masses treated?
Typically work-up will include imaging to better characterize the mass. A fine-needle biopsy may be indicated to better identify the source of neck mass. Depending on the cause of the neck mass, treatment may range from supportive care and observation, to use of antibiotics or surgical removal.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Dr Pham is excellent- extremely competent and smart while being personable and thorough."
— W. D.
Dr. Jennifer Goodrich

"needed immediate attention and got it. that’s the best. and at the end, Dr Goodrich offered to help get the patient to the car. and gave us a cell phone number to have direct contact with her as needed.
can it get any better than that?"
— S. C.
Dr. Jennifer Goodrich

"Dr Goodrich is so sweet and welcoming! She was open to all of my questions and made me feel very comfortable going into my septoplasty!"
— H.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Prompt; little wait time; excellent doctor."
— Z. S.
Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery

"Besides expert treatments, they have excellent visiting time management. Always a helpful staff when phone calling. Excellent follow up treatments and recovery success."
— B. F.
Dr. Jennifer Goodrich

"Dr. Goodrich is truly awesome! I can't thank her enough for correcting my years-long breathing issues. My nose surgery and follow-up went flawlessly. Every aspect of her world-class care from routine communications to friendly, responsive staff has been compassionate and caring. Thank you Dr. Goodrich and staff for taking such great care of me!"
— P. S.
Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery

"Great care. Entire staff make you feel comfortable."
— D. B.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Dr Pham truly has gone above and beyond to help me with my very complex case. She is also a plastic surgeon which gives her a unique understanding of the trauma that I had to not only to my sinuses and nose but also how the reconstruction of my facial bones plays into my sinus issues. She listens and is able to explain things easily and in a way that you can understand. I recommend her to my brother in law who broke his nose. He was soo happy with her work that he has recommended her to his friends. The office staff if very kind. I’ve had nothing but good experiences with her and her staff."
— A. G.
Dr. Jennifer Goodrich

"Definitely a Great Experience! Dr. Goodrich was awesome. Friendly and accommodating staff, Especially Joy.
I highly recommend Metro ENT and Facial Plastic Surgery.
I will definitely be back!"
— R. S.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Long time patient of Dr Pham and this practice. A wonderful team and medical professionals! Efficient, gracious, knowledgeable, and thorough."
— K. G.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Excellent care. Friendly staff, and clean environment. Dr. Pham Very knowledgeable in her field of work. Highly recommend"
— K. W.
Dr. Jennifer Goodrich

"Fantastic ENT care provided by Dr Jennifer Goodrich. She has helped me with expert care for ongoing sinus issues."
— E. H.
Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery

"I had a fantastic experience at Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery! From start to finish, the staff was welcoming, efficient, and truly caring. Dr. Andrew Lee and Dr. Jennifer Goodrich are a phenomenal team—knowledgeable, attentive, and patient. They took the time to really listen to my concerns and walked me through every step of my treatment plan with clarity and compassion. You can tell they’re passionate about what they do, and it shows in the quality of care they provide. I’m so grateful to have found this clinic—highly recommend to anyone looking for expert ENT care with a personal touch!"
— K. J.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Great doctor. Lovely office people"
— M. G.
Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery

"very nice experience."
— D. P.
Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery

"I’ve been coming to this practice for my sinus issues for years and very happy with the service. Now I also come here for my Botox shots and very satisfied with the results."
— J. C.
Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery

"Helpful and understanding."
— D. C. Q.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Great doctor and office staff. Never waited more than a few minutes and felt known, heard and understood ."
— J. M.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"I had a great experience with Dr. Pham and Dr. Lee. They were so nice and informative. I really appreciated how they took the time to explain everything to me. Can’t wait to go back!"
— D. M.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"She explained every thing clearly. Very knowledgeable and gentle during the procedure. Happy to know my condition can be improved so can’t wait to schedule my procedure on a Momday afternoon"
— H. D.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"The doctor is excellent and very knowledgeable."
— E. W.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Really grateful for Dr. Pham and all the office staff! She listens well and takes the time to explain her approach, answer questions and hear concerns."
— M. G.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Excellent with Dr Pham, as usual
Thank you"
— J. K.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Andrew Lee is the best!!"
— F. G.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee is really a great Doctor. He diagnosed my problem, offered a choice of treatments, understood my concerns, and worked to improve my breathing/sinus problems. He's also friendly and easy to talk to, and doesn't try to rush you. I would highly recommend him."
— M. W.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Responsive and professional. Obviously well informed and expert in quality of care."
— D. K.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee is very personable and answered all of my questions thoroughly. Appointments are quick but thorough. He has a nice bedside manner."
— M. C.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee was very thorough and explained everything very clearly. I would definitely him."
— S. V.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Same day appointment! 2 blood vessels in my nose coagulated to stop nosebleed. In and out in 15 minutes. Yay!"
— L. F.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee and all his staff was all amazing! They answered all my questions and even provided more to ease my mind."
— L. N.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Had ear pain, came, doc told me what’s causing it and recommended some meds, week later the pain gone. They know what they’re doing."
— K. A. E.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Outstanding visit, excellent diagnosis and medical care."
— A. M. L.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee and all of his supporting staff were amazing and made our consult and surgery a seamless experience. Dr. Lee took the time to hear our concerns and review the options with us. Everyone at the Surgery Center were warm and professional. Highly recommend!"
— R. M.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee is most kind and knowledgeable. He has addressed my sinuses and ears effectively and gently which is very important to me. Thank you Dr. Lee!"
— M. S.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee listened to my symptoms and concerns, answered all my questions patiently, and was informative and educated me on the various options for my situation. He has a good bedside manner. I felt well cared for."
— S.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"I got referred to Dr. Lee and he exceeded my expectations. He’s super knowledgeable, informative, and took time to explain everything thoroughly. Had a great experience with Dr. Lee.
I just got a procedure done = from start to finish he explained everything he was doing and made me feel super relaxed/comfortable during the procedure.
If yall need a GREAT ENT go to Dr. Lee. He will not disappoint!"
— G. K.
Dr. Esther Kim

Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Metro ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery is a very efficient and effective practice. On my second visit, I was seen immediately. Dr. Pham is a wonderful doctor. She took the time to explain the CT scan results, her diagnosis, and her treatment recommendation. She engaged me in a mutually beneficial discussion about my condition. I can’t say enough about her. Thank you."
— B. S.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"She is the Best ENT as her “bedside” manner, expertise and compassion set the gold star for providers!!!"
— B. S.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"My family has been going to see Dr. Pham for easily 11years. We trust her far and above anyone else to treat us for our ENT issues. She is a surgeon but still always finds a way to (even last minute) make time for us to handle the “little” issues. She has a way of making us feel important and gives us such great medical care!"
— R. M.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Dr. Pham is amazing. Beyond smart and so helpful anytime we come in. She treats my whole family. The office staff is also awesome."
— K. M.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee is a miracle worker! Almost 2 years of not having a sinus infection. The best part is that those medicines prescribed were natural, leading to long-term sustainability. Thank you, Dr. Lee."
— T. B.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"Dr. Lee was absolutely great. His team made the process very seamless and comforting when getting my young son’s tonsils removed. I was very impressed with the clinical team day of procedure. Dr. Lee was very honest, empathetic, and provided us with a great experience. Thank you!"
— A. L.
Dr. Andrew Yueh-Ling Lee

"The front desk was very helpful and friendly. I saw Dr. Lee, he’s very knowledgeable and personable. He takes his time to explain what’s going on and ALL the options to treat the problem, from the most affordable and easy to start, to the most expensive and complex treatments; which I really appreciated. I’m making this my ENT practice for now on."
— O. M.
Dr. Annette M. Pham

"Dr. Pham is hands down the most capable and caring medical professional I have ever encountered. As a woman, I have had my share of doctors who seemed to either not listen to my concerns or who outright blew them off. That is not Dr. Pham. When my infant son was having feeding issues, she worked with me to figure out the cause without any medical intervention. Two years later, she successfully performed his adenoidectomy, giving him immediate relief from symptoms that had delayed his speech and hearing but would likely have otherwise gone unnoticed. Always checking in on me during those appointments, too, she diagnosed my sinus issues and later performed my successful sinus surgery. More than once, for me and my son, she has found room to fit us into her already packed schedule for a same day urgent appointment. And each time, she remembers me and asks thoughtful follow-up questions. She feels like family. Her team as well is skilled and thoughtful, teeing up for when I have sent urgent messages, and I have never had a billing issue. Really, I don’t think you could find a better practitioner or practice."
— E. B.


